
Kuraray pools its expertise to create solutions for the automotive industry
The regulatory guidelines for vehicles are becoming increasingly strict and call for further development work to enhance safety and dependability as well as to reduce emissions, consumption and weight. Customers expect not only comfort and individual design, but also an ever higher standard of safety. Advances in technology are necessitating a re-think and forcing automotive manufacturers to establish competencies outside their traditional domains.
As a consequence, automotive manufacturers are focusing their product development on four areas: drive, lightweight construction, connectivity and driver assistance systems. Since over 75 percent of value is generated by component suppliers, innovative ideas are demanded. It is hoped that new materials will optimize vehicle performance. Lightweight materials have to be processed and utilized so that they optimize vehicle strength and performance.
“With Kuraray’s extensive range of high-performance materials, we are able to meet the growing needs of the automotive industry. Kuraray products yield numerous benefits for the automotive segment in the areas of performance, emission optimization, technology, safety and comfort,” explains Matthias Gutweiler, Managing Director of Kuraray Europe GmbH. “We support automotive innovation by partnering with our customers to find the best solutions for their applications.”
Weight reduction
“The lighter, the better” – every gram of weight counts in the battle to cut fuel consumption and meet global demands for emission reduction.
Reducing the weight of glass
Glass has always been an important material in the automotive industry. Large windshields, rear windows and panorama roofs admit plenty of light into the interior and impart comfort. But glass as a material is heavy, with an average of roughly 32 kg of glass going into each car today.
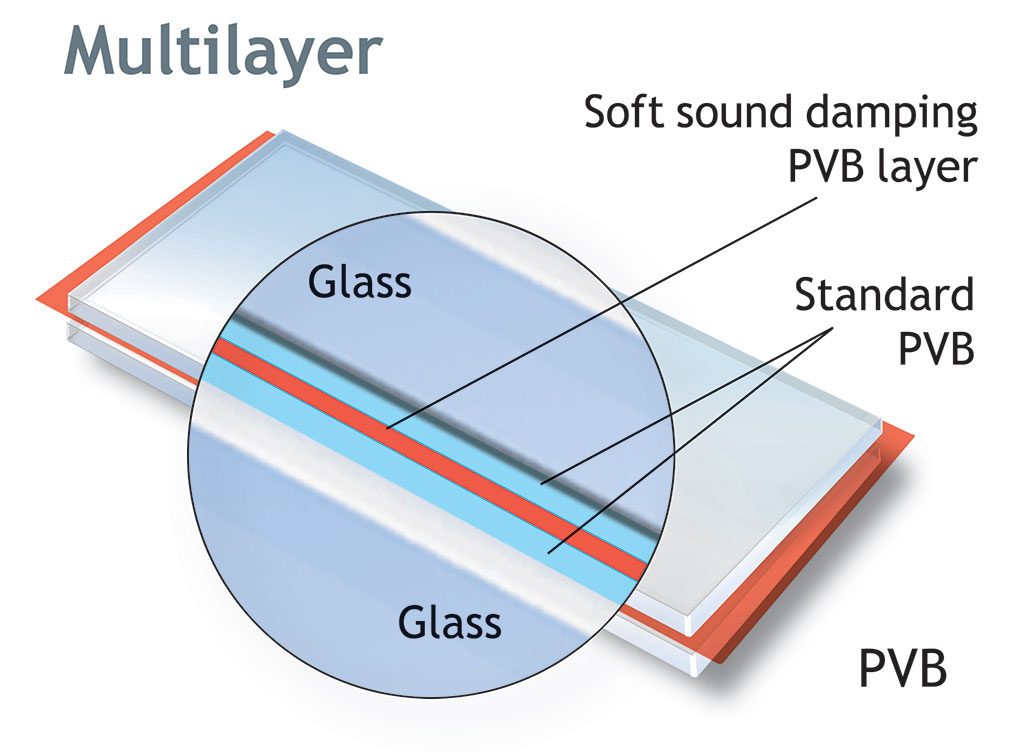
So how can the demand for lighter weight be reconciled with the advantages of glass as a material? Solutions with Trosifol® and SentryGlas® interlayers of polyvinyl butyral for laminated safety glass in windshields, side windows and sunroofs make this possible – the weight advantage today is about 12 percent over conventional laminated safety glass.
Further development work is targeted at reducing glass thickness and hence cutting weight further. The functionality of the film will make it possible to use even thinner and thus even lighter glass plies from now on. It is currently possible to reduce glass thickness to as little as 4 millimeters.
Furthermore, it is possible on sunroofs, for example, to replace a proportion of the glass with plastics. Trosifol® Spallshield® DPET composites are pre-assembled combinations of PVB, PET and a hard coat that are capable of reducing glass weight further.

Glass components fitted in the interior or at the rear can be fully replaced by transparent and/or hard, scratch-resistant plastics owing to their reduced safety requirements. Parapet® methacryl resins display greater transparency and surface hardness than other plastics and are used in cockpit and taillight applications, for example.
Substitutes for metal or plastics with higher relative density
Plastic has a number of advantages over metals, such as low weight and simple processing. It is therefore increasingly becoming the material of choice for fuel system components, for example, in motor vehicles.
The production of multi-layer plastic fuel tanks has grown enormously in importance in the automotive industry in recent years. Many automotive manufacturers have switched from fluorinated plastic monotanks or steel fuel tanks to multi-layer plastic tanks with an EVAL™ barrier layer. In Europe, 90 percent of all fuel tanks are made of plastic. In the USA, over 75 percent of motor vehicle fuel tanks are multi-layer plastic tanks with an EVAL™ barrier layer. The outstanding barrier characteristics of EVAL™ EVOH resins facilitate the production of lighter fuel tanks with very low evaporative emissions in compliance with strict international guidelines.
Engine components and parts of the fuel tank and transmission can also be made of plastic. GENESTAR™ is a high-performance polyamide resin with excellent resistance to heat and chemical influences, and low water uptake. GENESTAR™ can be used instead of aluminum die castings to reduce weight, and its integration in intercoolers can thus cut their weight by up to 40 percent. Its substitution of POM (polyoxymethylene) cuts the weight of fuel tubes by up to 30 percent, while thermostat housings made of GENESTAR™ are up to 20 percent lighter than those of conventional materials (PPS: polyphenylene sulfide). Its use in the drive elements of air conditioning systems permits a 40 percent weight reduction over conventional materials.
Acoustic components of Kuraray non-woven fabrics deliver not only good sound damping, but also significant weight savings. FELIBENDY™ is a grade of non-woven fabric that is produced using a high-temperature and high-pressure steam jet technology. This environmentally compatible material does without chemical adhesives and is suitable particularly for acoustic and thermal insulation in motor vehicles.
Bodywork/assembly
Synthetic fiber tapes with hook-and-loop fabric fasten body parts, interior trim and much more besides in automotive engineering. Kuraray’s MAGICTAPE™ hook-and-loop fasteners for the assembly of components in vehicle interiors improve design flexibility, boost productivity and reduce weight.
Bonding has become established as a key technology in vehicle construction and is steadily replacing other joining techniques such as welding and riveting. According to Industrieverband Klebstoffe e.V., a car today contains some 15 to 18 kilograms of adhesive.
Structural adhesives are used for bonding both engine and body parts and are replacing spot welds and mechanical fasteners. They join different and/or poorly weldable substrates such as high-strength steels, aluminum and magnesium (metal-to-metal bonding) as well as metals to composite materials (metal-to-composite bonding).
Compared to conventional joining methods, adhesives can therefore cut weight considerably. But this is not all, for they also enhance the flexibility of design engineering and safety in the vehicle as a whole – bonded vehicles generally perform better in crash tests.
Mowital® polyvinyl butyrals from Kuraray display outstanding adhesion to a multitude of surfaces and are an important component in the production of structural adhesives. During application, Mowital® helps to set the desired rheological properties as well as displaying the adhesion at a certain temperature necessary for joining. During final crosslinking (curing) with a second main component in the adhesive formulation, a unique, extra-strong chemical bond is established.
Emission reduction
Europe-wide directives and regulations to reduce air pollutants are applicable to all motor vehicles with gasoline or diesel engines and machines and devices. The output of pollutants is subject to ceilings for carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (CnHm), particulate mass (PM) and particle number (PN). The ceilings differ according to the type of engine and motor vehicle and are being constantly tightened, and not only in Europe.
According to calculations of the Federal Environment Agency in Berlin, 6 to 8 liters of gasoline can evaporate per vehicle per year under unfavorable conditions. Tank venting devices discharge evaporating or excess fuel vapor or gas (volatile hydrocarbons) not into the atmosphere but via a venting line straight to an activated carbon filter/canister filled with activated carbon. During refueling, pressure is necessarily generated, as the fuel nozzle forms a tight seal against the filler pipe. The fuel vapor is stored in the activated carbon and recirculated back to the combustion process when the engine is running. This prevents the emission of environmentally harmful fuel vapors from the tank – an activated carbon filter can intercept up to 90 percent of these evaporative emissions – and the vapors recirculated to the internal combustion engine can themselves be used as fuel. This also helps to reduce fuel consumption.
Activated carbon from Kuraray is extremely high-grade, and its characteristics can be adapted precisely to the respective regulatory requirements for exhaust gas cleaning in cars. For use in activated carbon filters or in canisters filled with activated carbon for tank venting, granulated and extruded grades are available.
The majority of plastic fuel tanks used today are made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), a stable and light-weight material. Since EVAL™’s gas barrier properties of HDPE are 4,400x stronger than HDPE, an EVAL™ layer in a multi-layer fuel tank yields a marked reduction in pollutant hydrocarbon emissions from the fuel tank. EVAL™ is recognized worldwide as the market-leading highly effective fuel emission barriers.
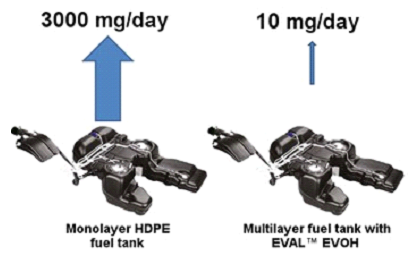
With EVAL™ barrier layers it is already possible to comply with tomorrow’s fuel emission standards. EVAL™ is used in multi-layer fuel tanks, multi-layer fuel lines and filler pipes.
Technological refinements, driver assistance systems
Augmented Reality arrived in the automotive industry with the advent of head-up displays. This technology, in use in fighter planes since the 1940s, allows information to be reflected into the driver’s field of vision. Since at a speed of 100 km/h the vehicle travels about 30 meters blind while the driver checks the speedometer, this represents a big step forward in terms of safety.
Trosifol® The Wedge™, a PVB laminating film, prevents double images from arising due to reflection against the inner and outer interfaces of the windshield. In close cooperation with automotive producers, the functionally critical wedge angle was defined in such a way that the virtual image appears to float with sharp outlines and high contrast near the front of the vehicle within the driver’s line of vision. Image location and brightness can be adjusted to suit the driver.
Tire performance
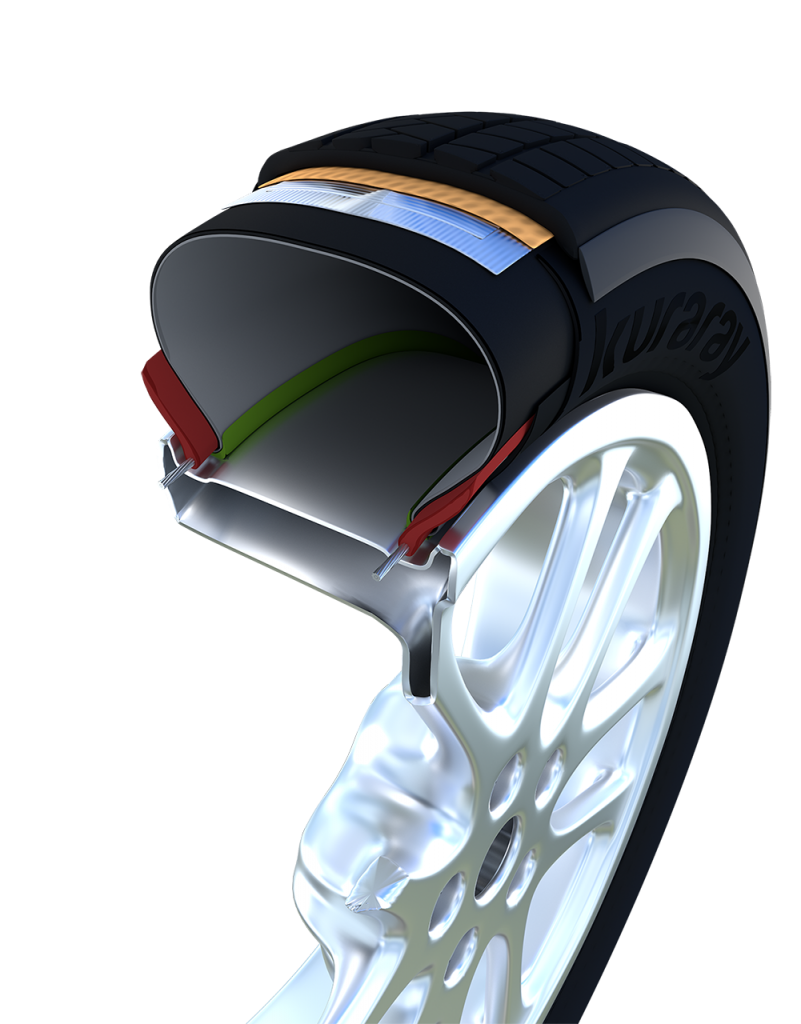

Car tires are high-tech entities. Grip, wear, rolling resistance and noise are parameters that manufacturers are constantly working on.
Kuraray Liquid Rubber, (LIR/LBR) highly viscous polymeric rubbers based on isoprene/butadiene, enhances tire performance significantly by simultaneously controlling the balance of grip, fuel efficiency and wear resistance.
Kuraray Liquid Rubber (K-LR) comprises Liquid Isoprene Rubber (L-IR), Liquid Butadiene Rubber (L-BR) and Liquid Styrene Butadiene Rubber (L-SBR). These high-viscosity synthetic rubbers are based on isoprene, butadiene and styrene. They are colorless, transparent and almost entirely odorless, with low VOC’s.
Kuraray’s liquid rubber grades (L-IR/L-BR/L-SBR )function as reactive plasticizers but have far higher molecular weight than normal plasticizers. They are co-vulcanizable and reduce migration significantly which improves the product’s shelf life.
Using K-LR during the rubber compounding phase significantly reduces processing time, while maintaining the rubber compounds’ physical properties. This results in a product with lower processing costs.
L-IR/L-BR/L-SBR can be crosslinked with all conventional rubber types. As a special feature, L-IR/L-BR/L-SBR are also available functionalized and thus facilitate adhesion to various substances, especially metal surfaces.
Comfort
Travel comfort can be achieved in a variety of ways. Technical functions, high-grade interior furnishing/equipment and noise damping communicate quality and, in combination with enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced CO2 emissions, offer the complete package that consumers want.
Polyols from Kuraray raise the performance of polyurethanes used for coating vehicle seats by optimizing their suppleness and long-term stability. These polymers derived from 3-methyl-1,5-pentanediol (MPD) impart distinctive properties to the methyl group, such as low viscosity, resistance to hydrolysis, wide-ranging compatibility and an agreeable softness.
Noise reduction
Noise impairs travel comfort considerably and can damage health. In addition to road noise, components in the interior can cause unwanted squeaking or creaking noises and be distracting.
Laminated safety glass with Trosifol® interlayers not only delivers greater safety coupled with lower
Decorative film solutions made of SEPTON™ (hydrogenated styrene block copolymers) not only protect stressed surfaces, but also prevent annoying noise in the interior. SEPTON™ films are distinguished by their high scratch and abrasion resistance. Noise reduction is achieved either through their vibration-damping effect or by reducing the frictional resistance.
Sound-absorbing Felibendy composites of needlefelt and PBT melt-blown fibers are used for the production of acoustic components. Their weight and thickness can be varied to achieve different sound absorption levels.








